What Is the Only Internal Organ Capable of Regenerating Lost Again
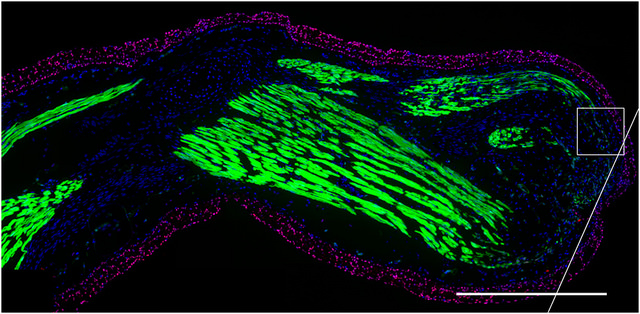
In that location are many animals that tin regenerate circuitous trunk parts with total role and form after amputation or injury. Invertebrates (animals without a spinal string) such equally the flatworm or planarian tin regenerate both the caput from a tail piece, and the tail from a head slice. Among vertebrates (animals with a spinal cord), fish tin can regenerate parts of the brain, eye, kidney, heart and fins. Frogs tin can regenerate the limb, tail, encephalon and eye tissue as tadpoles merely non as adults. And salamanders tin can regenerate the limb, center, tail, brain, eye tissues, kidney, brain and spinal cord throughout life.
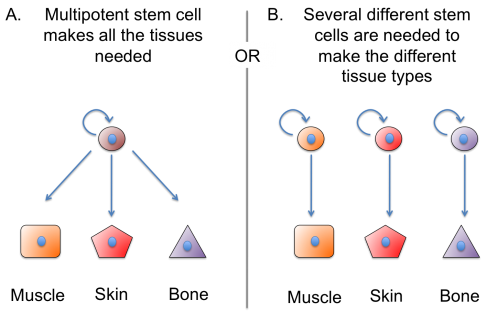
How do these regenerative animals regrow such complex structures? Afterward amputation, stem cells accumulate at the injury site in a structure called the blastema. An important subject of ongoing enquiry is how signals from the injury site cause the stem cells to form the blastema and start dividing to rebuild the missing part. And what virtually the stalk cells themselves? Practise the animals use a unmarried type of stalk jail cell in the blastema that can differentiate into many dissimilar types of tissues (chosen a multipotent stem cell). Or is a separate set of stem cells responsible for making each of the different tissues needed to make up the new body part?
Recent inquiry in dissimilar regenerating animals has shown that at that place are various stem cell strategies for regenerating body parts built from multiple tissues, such equally muscle, nerve and pare. If we empathise the principles and molecules these animals use to regenerate adult tissues, can these lessons exist practical to regenerating or applied science human tissue?
Scientist Peter Reddien's research group in the United states of america recently solved a long-standing question in planarian (flatworm) regeneration – can a single stalk cell regenerate a whole animal? The answer is yeah, it tin. This shows that adult planaria have pluripotent stem cells – cells that tin make ALL the prison cell types of the animal's body. How these pluripotent cells are controlled in the flatworm'due south body so that they do non course tumors is an important question that several inquiry groups are now studying.
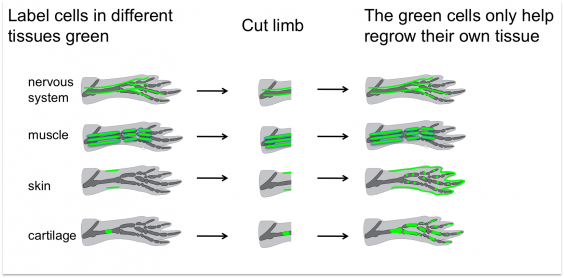
Simply non all animals apply pluripotent cells in regeneration. The stem cells that regenerate a frog tail and a salamander limb have very different properties from a planarian stem cell. In these animals, each tissue – such every bit muscle, nervus, or pare – has its ain fix of stem cells that merely make the different types of cells in that particular tissue. In other words, a muscle stem cell cannot make skin and skin stem cells tin't make musculus. These multipotent tissue-specific stem cells are probably very similar to the stalk cells in our ain bodies that renew or repair tissues such every bit our skin or muscle. Why can such stem cells regenerate an entire limb in a salamander, but only repair harm to a single tissue type in our own bodies? This is another question that scientists are working on now.
Besides as using stem cells, regeneration tin work past causing differentiated cells that had stopped dividing to 'go back' to dividing and multiplying in gild to replace the lost tissue. This has recently been shown to happen in centre regeneration in zebrafish, where a eye muscle cell called the cardiomyocyte divides to replenish missing cardiac tissue. This regenerative phenomenon has also been institute in newly built-in mouse hearts, but is rapidly lost equally the mice mature. More research is needed to sympathize how differentiated cells tin exist made to carve up and produce new heart tissue, and why this chapters is lost in humans.
Past defining the properties of stem cells that regenerate complex body parts, scientists are learning how injury causes these stem cells to regenerate the missing part instead of just forming scar tissue. Future research may brand it possible to apply this knowledge in new kinds of medical treatments.
Pluripotent stem cells
How similar are the pluripotent stalk cells of the planarian to mammalian embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells? By studying the planarian, maybe we will proceeds insight into how to control human embryonic stalk cells to replace parts of our own bodies.
Tissue stem cells
Salamanders and frogs utilize tissue stem cells that may exist much similar our own, so why can they regenerate a whole limb whereas we form scars? Ongoing research indicates that regenerative animals go on a kind of map inside their adult tissues, telling cells where they are and what they should be. Parts of this map may have been lost in mammals, or perhaps our stem cells have lost the ability to read the map. Researchers hope to observe out what exactly is missing or blocked in mammals, and whether such information tin can be restored to direct stem cells to take part in regeneration for medical applications.
Differentiated cells
Can we brand adult, differentiated cells similar heart muscle cells start dividing once again, as in the zebrafish? It will exist of import to find out why mammalian heart cells lose this ability, and if it can exist restored.
Source: https://www.eurostemcell.org/regeneration-what-does-it-mean-and-how-does-it-work
0 Response to "What Is the Only Internal Organ Capable of Regenerating Lost Again"
Post a Comment